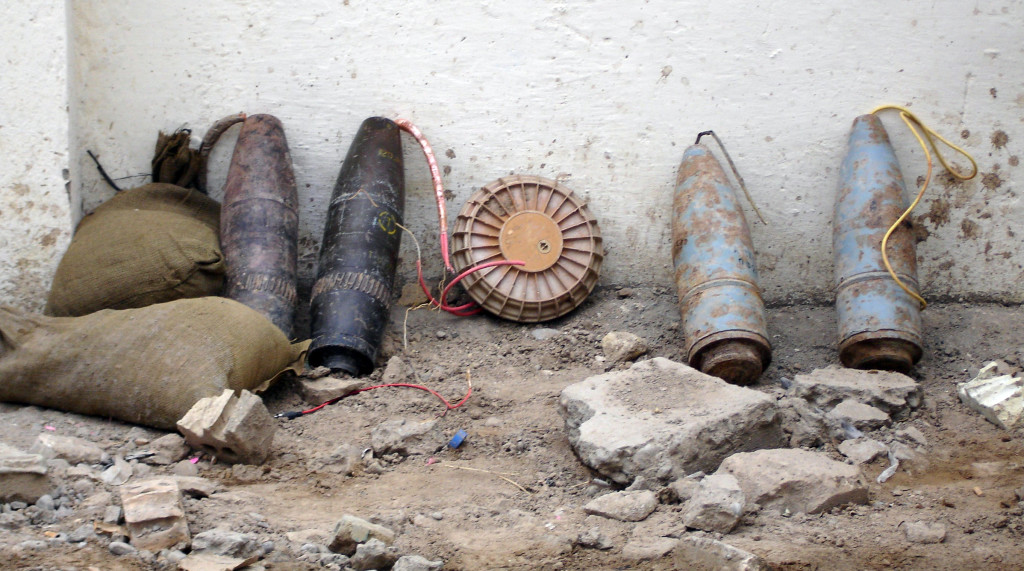
“IED Baghdad from munitions”. Licensed under Public Domain via Commons – https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:IED_Baghdad_from_munitions.jpg#/media/File:IED_Baghdad_from_munitions.jpg
WASHINGTON – Chemicals are an important part of modern society but, in the wrong hands, they can be deadly weapons. The government has recognized this danger and taken on the act of trying to protect the American people by protecting the stocks of chemicals across the country.
Since the 9/11 attacks the United States has collectively feared a repeat terrorist attack on domestic soil. In, then-President George W. Bush called for the creation of what is now called the Department of Homeland Security to address and attempt to resolve this very fear.
Part of that effort includes the work done by the Office of Infrastructure Protection, which has a mission to work with the chemical industry to protect critical infrastructure, including chemical facilities, from terrorist attacks.
A key piece of the critical infrastructure that needs to be protected is chemical facilities.
“We are talking about things where people could turn a facility into a weapon much like the terrorists in 9/11. They took something that we would not have expected to be used as a weapon and turned it into [a weapon]. And this presents a significant concern for the department,” said Todd Klessman, a senior policy advisor at the Department of Homeland Security.
He said there are two main concerns when it comes to chemical site facilities. The first is the prevention of an attack directly on the facility. Some of these sites are located in heavily populated urban areas. A release of a toxic gas or substance would result in many people injured or dead. Experts point to the Bhopal disaster in India in 1984, in which a gas leak at a pesticide plant killed at least 3,787 people and injured more than 550,000 others.
The second concern is a terrorist stealing chemicals to build a bomb elsewhere, Klessman said at a talk about chemical weapons and security at the Center for Strategic and International Studies, a Washington based think tank.
Acknowledging this infrastructure vulnerability, Congress authorized the creation of the Chemical Facility Anti-Terrorism Standards program in 2007 and reauthorized it for an additional four years in 2014. This legislation gave DHS regulatory authority over “high-risk chemical facilities.” The first task was to determine what that category meant.
“What we decided was that it didn’t really matter what type of facility these chemicals were at. The chemicals will present threats or risk based on their nature, not necessarily the type of facility,” said Klessman, in an interview.
The department developed a list of 325 chemicals of interest and set out to base their regulator efforts on this list, rather than on categories of facilities. Each of the chemicals on the list presented a security risk in at least one of three categories:
- Release hazards – Toxics, flammables and explosives
- Theft aversion hazards – Precursors to chemical weapons, explosives, improvised explosive devices (IEDs) or weapons of mass destruction
- Sabotage hazards – Chemicals that when mixed with water will turn into toxic hazards
This results in DHS regulating a large swath of industry that is not just limited to what would traditionally be classified as chemical facilities. Alongside the many manufacturing facilities regulated are mines, education facilities, prisons and wineries.
Once the department has determined that a facility is within the highest risk category, it works with a company to implement an appropriate security plan. There are about 3,000 facilities in the high-risk category with only 111 falling into the highest risk group.
“Rather than give prescriptive standards and tell a facility that they must have this type of fence or they must have this type of camera system, we’ve identified 18 areas of security and asked the facility to tell us how they are going to address this,” said Klessman. This allows the facilities to build up on what they already have in place and recognizes that this is not a one size fits all security solution.
“It also makes it so that the terrorists cannot simply read our manual and determine how they can overcome our security,” he said. “If we had a requirement of a ten foot fence then the terrorist could just go build an 11-foot ladder.”