This week marks the 65th anniversary of the end of the Korean War, and the 20th anniversary of the Korean War Veterans Memorial. Service members and families gathered at the memorial over the weekend to hear the names read of the fallen soldiers. The Korean War Veterans Memorial Foundation is currently pushing legislation that would allow them to build a glass wall around the memorial with these names listed.
Medill National Security Reporting Project
 Medill/GlobalPost investigation sheds new light on $3.2 billion U.S. mine clearance and victim assistance effort.
Medill/GlobalPost investigation sheds new light on $3.2 billion U.S. mine clearance and victim assistance effort.
→ Visit the project site
→ Read more about the project
 Medill/USA TODAY investigation of U.S. international food aid programs finds significant, entrenched problems
Read about the project.
Medill/USA TODAY investigation of U.S. international food aid programs finds significant, entrenched problems
Read about the project.Like and follow us
R.I.P. James Wright Foley, 1973-2014
#MedillRemembers James Foley, One Year Later
Remembering James Foley's life and legacy one year after his death at the hands of the Islamic State.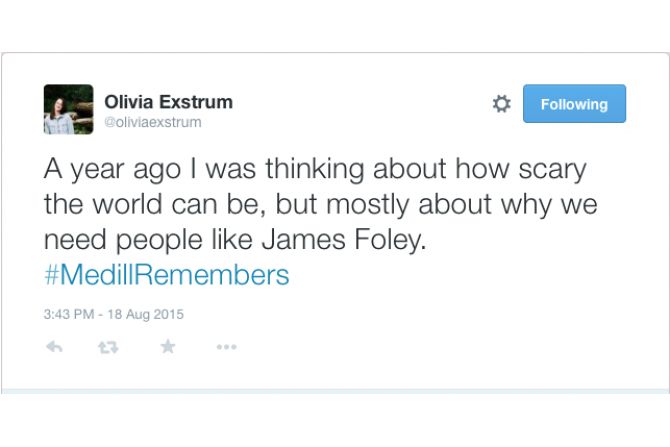 → Continue to the story.
→ Continue to the story.
→ James Foley: A legacy that lives on (VIDEO)
Major TV networks sign onto freelancer safety compact
Read about the compact, which was signed by Medill NSJI Co-Director Ellen Shearer at Columbia University in September, here.-
Real-time Twitter feed
NSJI in the News
The Voice of America featured NSJI in a recent article about how it prepares journalists to cover stories in conflict zones.McCormick Foundation renews grant for Medill National Security Journalism program
EVANSTON, Ill. — The Robert R. McCormick Foundation has renewed a $1 million grant to fund the Medill National Security Journalism Initiative at Northwestern University over the next two years.

The NSJ program provides journalists-in-training and working journalists with the knowledge and skills necessary to report accurately, completely and with context on events and issues related to defense, security and civil liberties. The initiative began in January, 2009 with an initial three-year, $1.3 million McCormick Foundation grant. The grant was also renewed for $1 million over two years in 2011.
About the initiative
By the Medill National Security Journalism Initiative, in partnership with the McCormick Foundation.Links we recommend
- Campaign for Innocent Victims in Conflict
- Global Warning
- International Reporting Project
- McCormick Foundation
- Medill
- Medill Washington
- Military Reporters & Editors
- Northwestern University
- Security Clearance
- The Center for Public Integrity
- The Crimes of War Projct
- The Dart Center
- Washington Post National Security news




